Video Intelligent Analysis
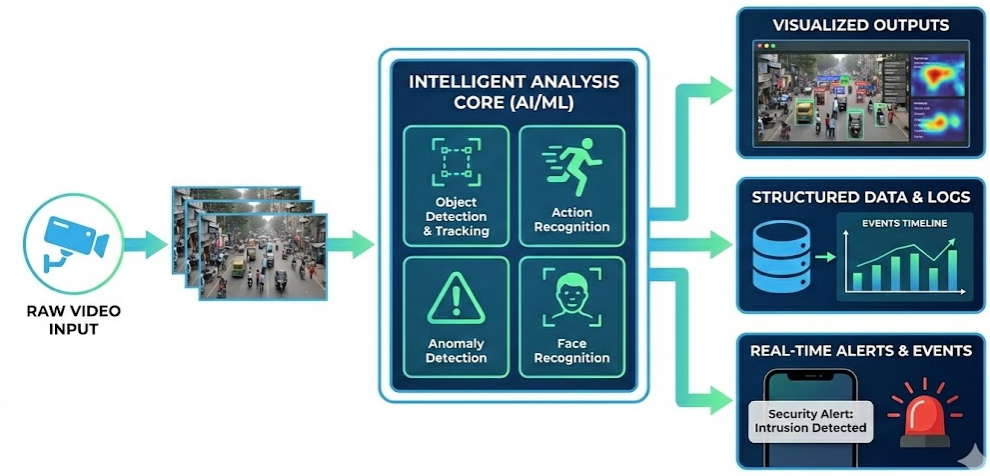
VIA Framework Diagram
Task Description
Video Intelligent Analysis focuses on the comprehensive analysis of content captured through video surveillance, providing essential support for the reliable "Smart Mind and Super Vision · Fire Eye" video monitoring system. This system plays a pivotal role in ensuring the effectiveness and accuracy of surveillance by leveraging advanced AI technologies to detect, recognize, and track objects and individuals across different environments. Our research spans several key areas, including Small Object Detection, which aims to identify and track objects that are typically hard to detect due to their size; Pedestrian Detection, which focuses on detecting pedestrians in diverse settings; Face Super-Resolution, designed to enhance the resolution and clarity of facial images for better identification; and Person Re-Identification, which seeks to match individuals across multiple camera views, regardless of variations in lighting, posture, or background.
Selected Papers
Exceptional Contribution
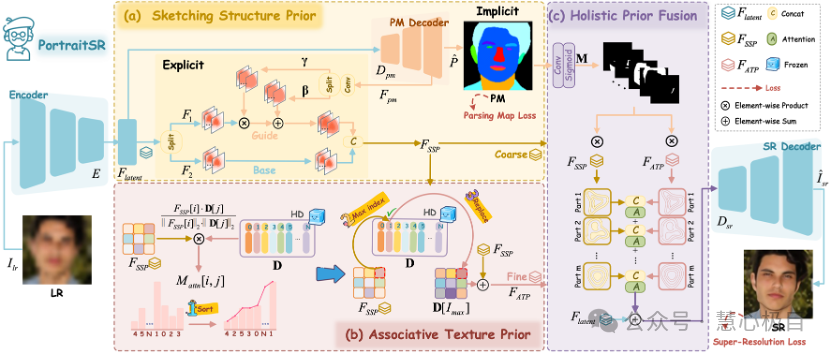
PortraitSR: Artist-Inspired Prior Learning for Progressive Face Super-Resolution
MiaoQing Wang, Shuang Li, ChangJiang Kuang,Long Sun,JiaXu Leng*Face super-resolution aims to reconstruct high-resolution face images from low-resolution inputs. Although existing methods have advanced this task through architectural innovations and generative modeling, they may produce structures with semantic inconsistencies and unrealistic textures, especially at high magnification factors. To mitigate these limitations, we draw inspiration from the human artistic process of 'structure first, then detail,' and propose a progressive prior-guided restoration strategy. Specifically, we first introduce a Sketch Structure Prior (SSP) module, which embeds global semantics and refines local geometry through implicit parsing guidance and explicit spatial modulation. Next, an Associated Texture Prior (ATP) module leverages a high-quality dictionary (HD) learned from high-quality reconstructions to guide fine-grained detail recovery. Finally, to unify structure and detail features, we design a Holistic Prior Fusion (HPF) module, which adaptively integrates them into semantically consistent facial regions. Extensive evaluations on the CelebA and Helen datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance in both structural fidelity and texture realism compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches.
Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence(AAAI),2026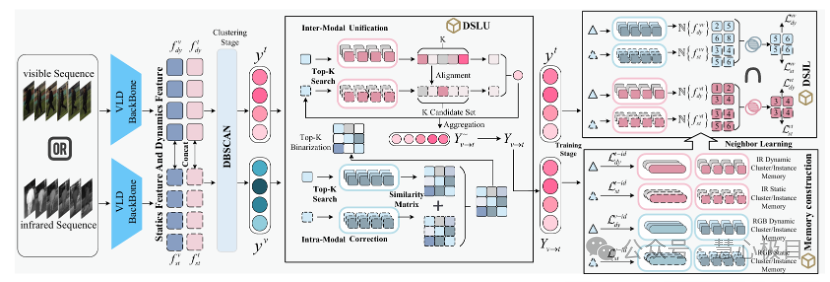
DSC:Dynamic-Static Collaboration for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Video-Based Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
JiaXu Leng, ZhengJie Wang, Shuang Li, Xinbo Gao*Focusing on the problem of cross-modal person sequence retrieval in all-day intelligent surveillance, we propose the first unsupervised domain-adaptive video visible-infrared person re-identification task (UDA-VVI-ReID). Traditional video-level methods rely on supervised approaches and achieve video-level matching by simply averaging frame-level features, which are easily affected by occlusions and modal differences, resulting in high pseudo-label noise and limited retrieval performance. To address this, we propose an unsupervised dynamic-static collaboration framework (DSC). The dynamic-static label unification module (DSLU) filters high-confidence pseudo-labels by verifying the consistency between motion and appearance predictions, while the dynamic-static joint learning module (DSJL) promotes cross-modal alignment and local structure consistency in both dynamic and static feature spaces through neighbor-aware contrastive learning. Experimental results on the HITSZ-VCM and BUPTCampus video cross-modal datasets demonstrate that DSC significantly outperforms existing methods under the unsupervised setting and even surpasses some supervised models.
Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence(AAAI),2026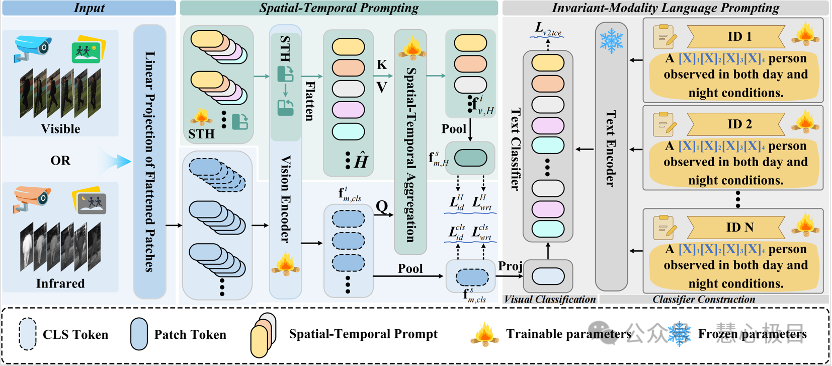
Video-Level Language-Driven Video-Based Visible-Infrared Person
Re-Identification

Shuang Li, Jiaxu Leng, Changjiang Kuang, Mingpi Tan, Xinbo Gao*
Faced with the increasing demand for all-day intelligent surveillance, Video-Based Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification (VVI-ReID), as a key technology for achieving unified identification in both daytime and nighttime video surveillance, has long been challenged by modality discrepancies and insufficient temporal modeling. To address this, this paper proposes a novel Video-Level Language-Driven VVI-ReID (VLD) framework. This method introduces video-level language descriptions for the first time in the VVI-ReID task as a cross-modality bridge, leveraging the CLIP multimodal pre-trained model to generate unified language prompts, and semantically modeling person identities in natural language to achieve deep semantic alignment between infrared and visible images. The method consists of two core modules: the Invariant-Modality Language Prompting (IMLP) module and the Spatio-Temporal Prompting (STP) module, which respectively enhance the discriminative capability of cross-modality features and the inter-frame information fusion from the perspectives of semantic consistency and spatio-temporal modeling. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches on the HITSZ-VCM and BUPTCampus public datasets, while reducing training time to just 2 hours and increasing parameters by only 2.39M, effectively balancing performance and computational resource consumption, making it suitable for practical applications.
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security(TIFS),2025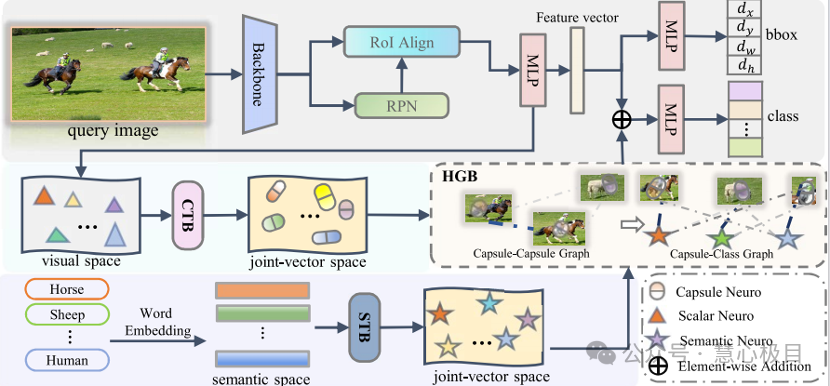
GCapNet-FSD: A Heterogeneous Graph Capsule Network for Few-Shot
Object Detection

Shuang Li, Jiaxu Leng, Ji Gan, Mengjingcheng Mo, Xinbo Gao*
TVisible-Infrared Person Re-Identification (VI-ReID) plays a crucial role in around-the-clock surveillance systems. However, existing methods mainly focus on learning appearance features, often neglecting body shape features. Shape features not only complement appearance features but also naturally exhibit robustness against modality differences. Despite their potential, effectively integrating shape and appearance features still faces many challenges. Appearance features are easily affected by modality differences and background noise, while shape features often suffer from inaccurate shape estimations in infrared images due to the limitations of auxiliary models. To address these issues, this paper proposes a shape-centric representation learning framework, ScRL, which effectively improves VI-ReID performance by innovatively integrating shape and appearance features. Specifically, we introduce the Infrared Shape Restoration (ISR) module, which repairs errors in shape representations at the feature level by leveraging appearance features in infrared images; propose the Shape Feature Propagation (SFP) module, enabling the model to directly extract shape features from the original images during inference without auxiliary models; and design the Appearance Feature Enhancement (AFE) module, which uses shape features to strengthen identity-related appearance information while effectively suppressing identity-unrelated noise. Thanks to the effective integration of shape and appearance features, ScRL surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods on multiple benchmark datasets.
Neural Networks,2025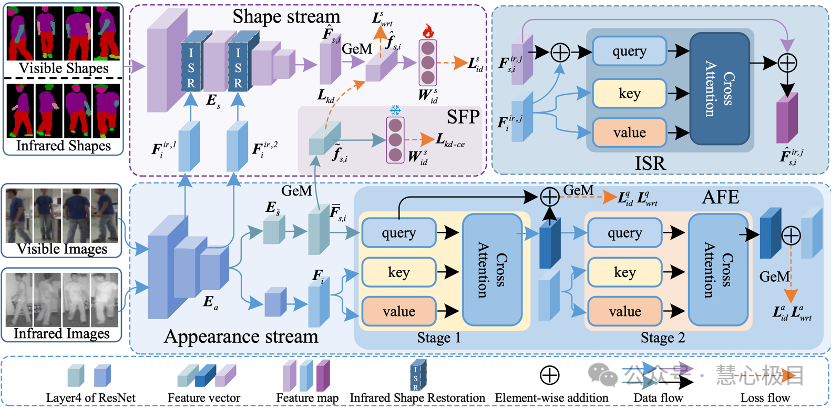
Shape-centered Representation Learning for Visible-Infrared Person
Re-Identification

Shuang Li, Jiaxu Leng, Ji Gan, Mengjingcheng Mo, Xinbo Gao*
TVisible-Infrared Person Re-Identification (VI-ReID) plays a crucial role in around-the-clock surveillance systems. However, existing methods mainly focus on learning appearance features, often neglecting body shape features. Shape features not only complement appearance features but also naturally exhibit robustness against modality differences. Despite their potential, effectively integrating shape and appearance features still faces many challenges. Appearance features are easily affected by modality differences and background noise, while shape features often suffer from inaccurate shape estimations in infrared images due to the limitations of auxiliary models. To address these issues, this paper proposes a shape-centric representation learning framework, ScRL, which effectively improves VI-ReID performance by innovatively integrating shape and appearance features. Specifically, we introduce the Infrared Shape Restoration (ISR) module, which repairs errors in shape representations at the feature level by leveraging appearance features in infrared images; propose the Shape Feature Propagation (SFP) module, enabling the model to directly extract shape features from the original images during inference without auxiliary models; and design the Appearance Feature Enhancement (AFE) module, which uses shape features to strengthen identity-related appearance information while effectively suppressing identity-unrelated noise. Thanks to the effective integration of shape and appearance features, ScRL surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods on multiple benchmark datasets.
Pattern Recognition,2025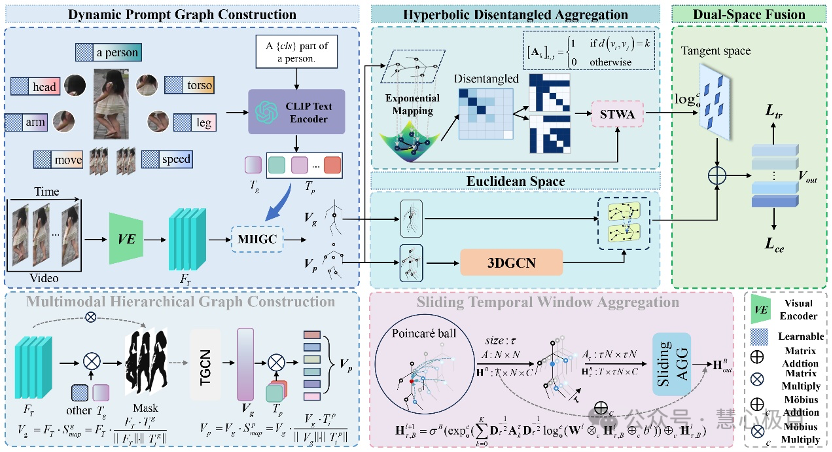
Dual-Space Video Person Re-Identification

Jiaxu Leng, Changjiang Kuang, Shuang Li, Ji Gan, Haosheng Chen & Xinbo Gao*
Traditional methods mainly rely on Euclidean space for representation learning, but they fall short when dealing with complex hierarchical relationships such as occlusion and background interference. DS-VReID combines the advantages of Euclidean and hyperbolic geometry, leveraging the negative curvature characteristics of hyperbolic space to excel at capturing complex hierarchical structures, significantly enhancing the identity discriminability of features. Specifically, the proposed DPGC module constructs structural relationships using a pre-trained CLIP model and dynamic prompts, while the HDA module accurately models spatiotemporal hierarchical relationships by decoupling node distances and integrating adjacency matrices, addressing long-distance dependency issues in hyperbolic space. Experimental results demonstrate that DS-VReID surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods on multiple benchmark datasets.
International Journal of Computer Vision,2025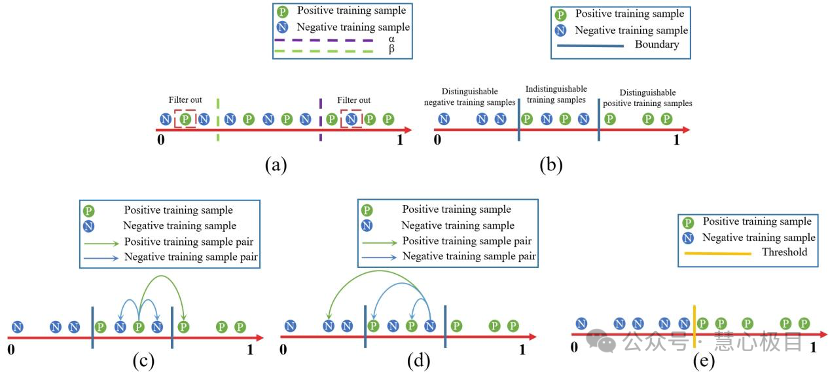
RC-DETR: Improving DETRs in Crowded Pedestrian Detection via
Rank-based Contrastive Learning

Feng Gao, Jiaxu Leng, Ji Gan, Xinbo Gao*
DETR-based detectors experience a significant decline in performance in crowded scenes because, during training, there is only a single category label (pedestrian) constraining the positive training samples. This causes positive training samples with large shape differences (pedestrians) to have difficulty producing similar image features, while positive training samples with similar shapes (pedestrians) and negative training samples (background) may produce similar image features, leading to false detections. To address this issue, this paper proposes a ranking-based contrastive learning method that builds an additional constraint for each hard-to-distinguish training sample to generate distinguishable image features. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method effectively improves the performance of the baseline on four challenging pedestrian detection datasets and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Neural Networks, 2024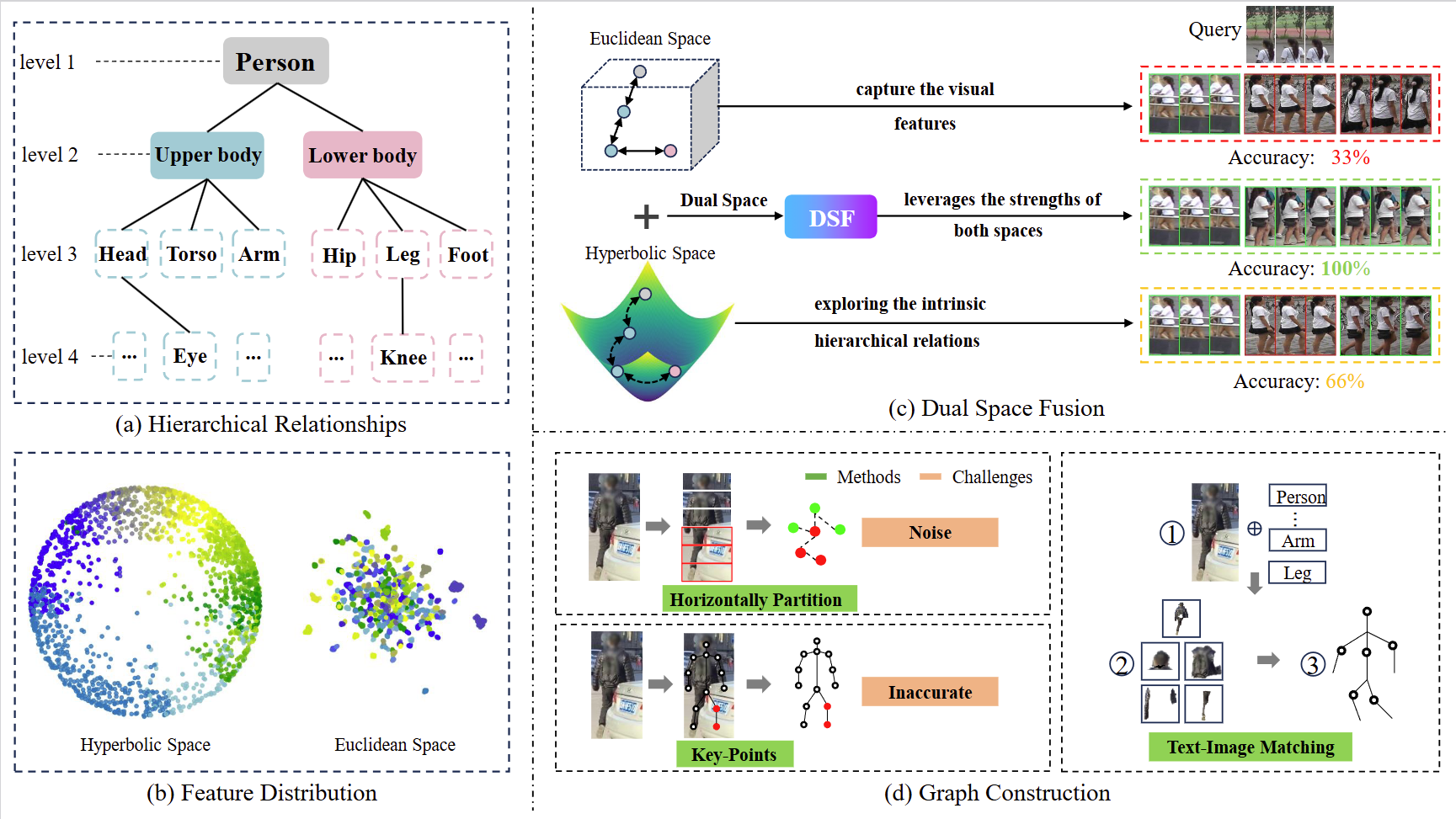
Dual-Space Video Person Re-identification

Jiaxu Leng, Changjiang Kuang, Shuang Li, Ji Gan, Haosheng Chen and Xinbo
Gao*
Video person re-identification (VReID) aims to recognize individuals across video sequences. Existing methods primarily use Euclidean space for representation learning but struggle to capture complex hierarchical structures, especially in scenarios with occlusions and background clutter. In contrast, hyperbolic space, with its negatively curved geometry, excels at preserving hierarchical relationships and enhancing discrimination between similar appearances. Inspired by these, we propose Dual-Space Video Person Re-Identification (DS-VReID) to utilize the strength of both Euclidean and hyperbolic geometries, capturing the visual features while also exploring the intrinsic hierarchical relations, thereby enhancing the discriminative capacity of the features. Specifically, we design the Dynamic Prompt Graph Construction (DPGC) module, which uses a pre-trained CLIP model with learnable dynamic prompts to construct 3D graphs that capture subtle changes and dynamic information in video sequences. Building upon this, we introduce the Hyperbolic Disentangled Aggregation (HDA) module, which addresses long-range dependency modeling by decoupling node distances and integrating adjacency matrices, capturing detailed spatial-temporal hierarchical relationships.
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 2025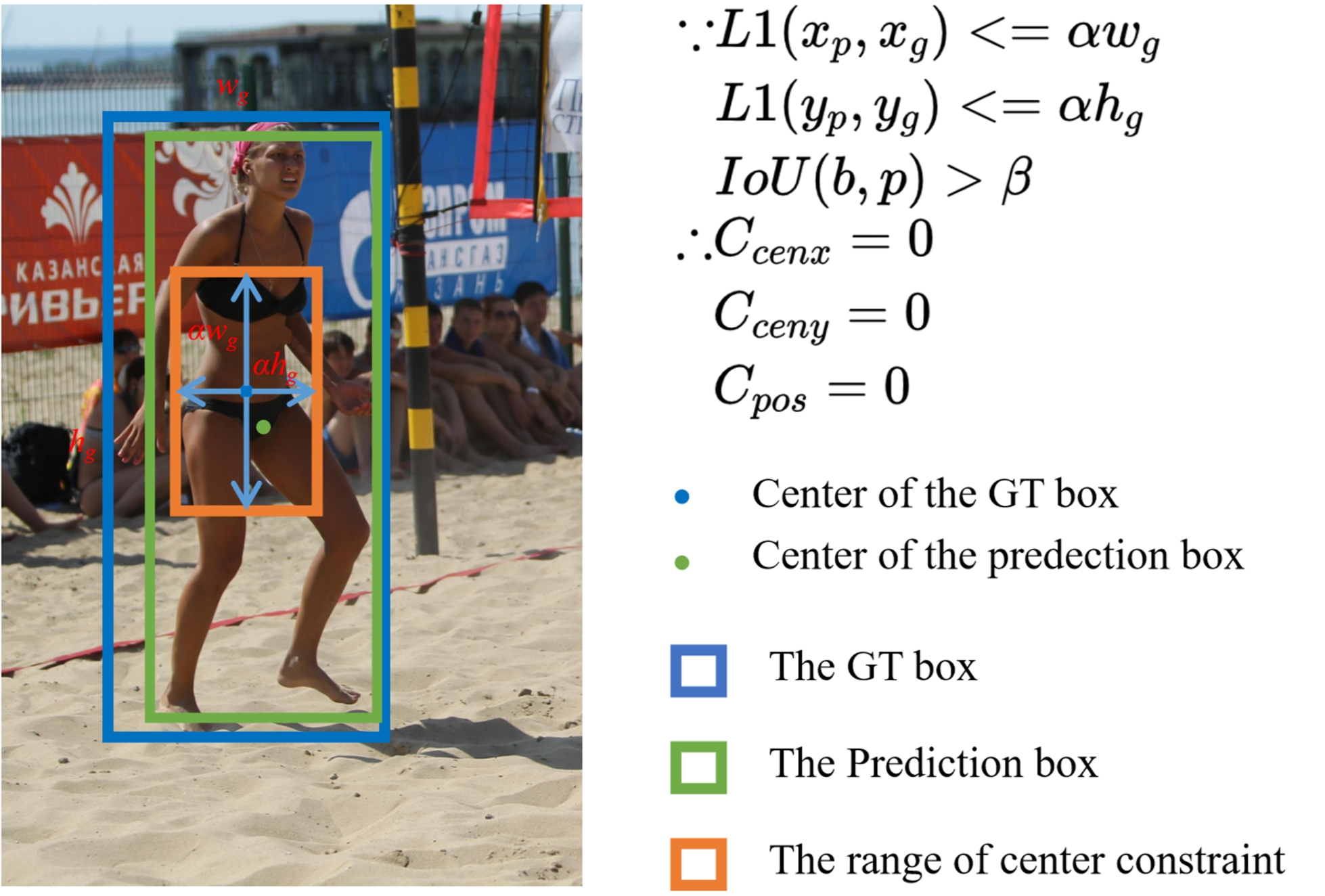
Selecting Learnable Training Samples is All DETRs Need in Crowded
Pedestrian Detection

Feng Gao, Jiaxu Leng*, Ji Gan, and Xinbo Gao*
DEtection TRansformer (DETR) and its variants (DETRs) achieved impressive performance in general object detection. However, in crowded pedestrian detection, the performance of DETRs is still unsatisfactory due to the inappropriate sample selection method which results in more false positives. To settle the issue, we proposed a simple but effective sample selection method for DETRs, Sample Selection for Crowded Pedestrians (SSCP), which consists of the constraint-guided label assignment scheme (CGLA) and the utilizability-aware focal loss (UAFL). Our core idea is to select learnable samples for DETRs and adaptively regulate the loss weights of samples based on their utilizability. Specifically, in CGLA, we proposed a new cost function to ensure that only learnable positive training samples are retained and the rest are negative training samples. Further, considering the utilizability of samples, we designed UAFL to adaptively assign different loss weights to learnable positive samples depending on their gradient ratio and IoU.
ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), 2023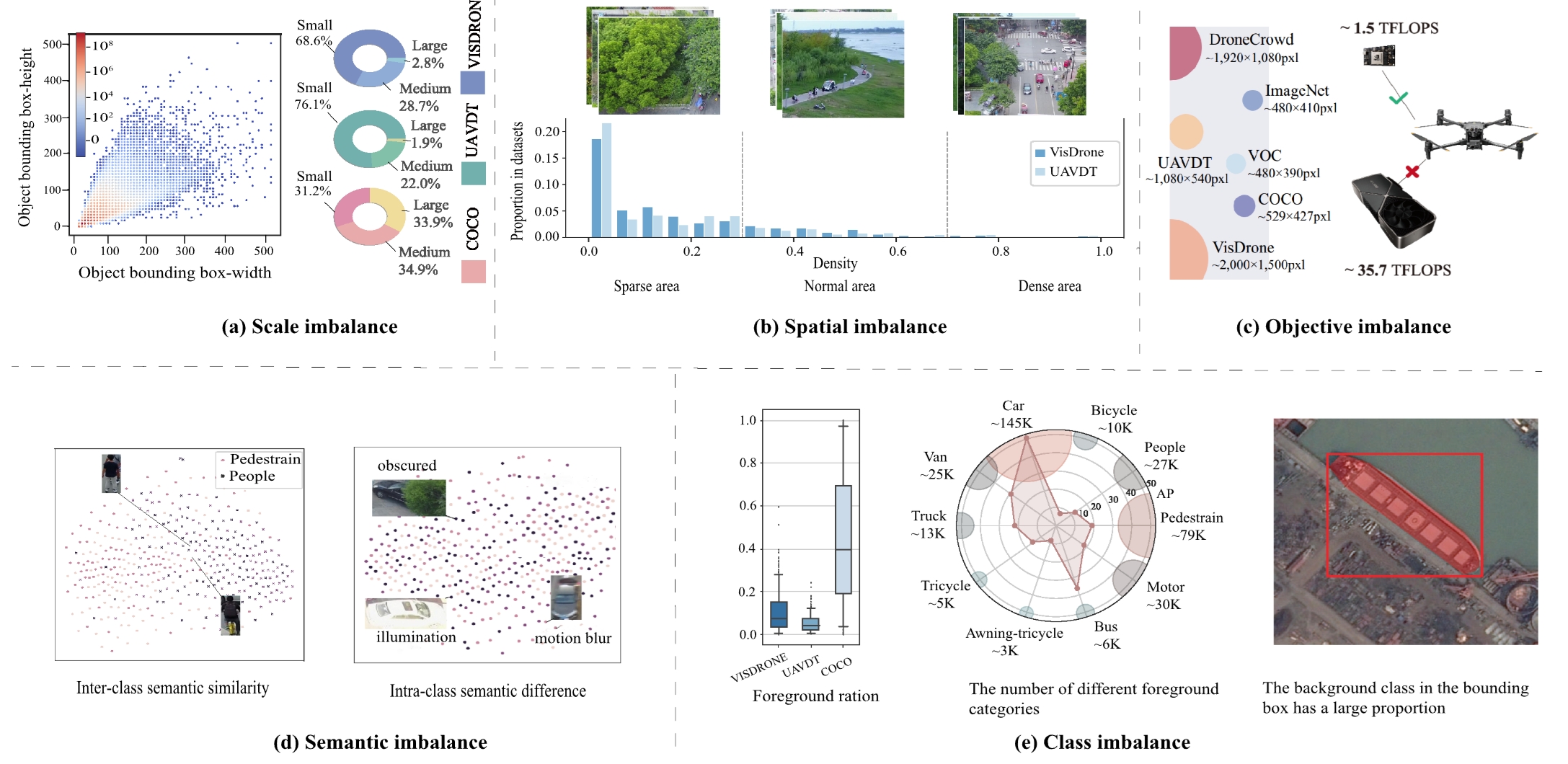
Recent Advances for Aerial Object Detection: A Survey

Jiaxu Leng, Yongming Ye, Mengjingcheng Mo, Chengqiang Gao, Ji Gan, Bin Xiao
and Xinbo Gao*
Aerial object detection, as object detection in aerial images captured from an overhead perspective, has been widely applied in urban management, industrial inspection, and other aspects. However, the performance of existing aerial object detection algorithms is hindered by variations in object scales and orientations attributed to the aerial perspective. This survey presents a comprehensive review of recent advances in aerial object detection. We start with some basic concepts of aerial object detection and then summarize the five imbalance problems of aerial object detection, including scale imbalance, spatial imbalance, objective imbalance, semantic imbalance, and class imbalance. Moreover, we classify and analyze relevant methods and especially introduce the applications of aerial object detection in practical scenarios. Finally, the performance evaluation is presented on two popular aerial object detection datasets VisDrone-DET and DOTA, and we discuss several future directions that could facilitate the development of aerial object detection.
ACM Computing Surveys, 2024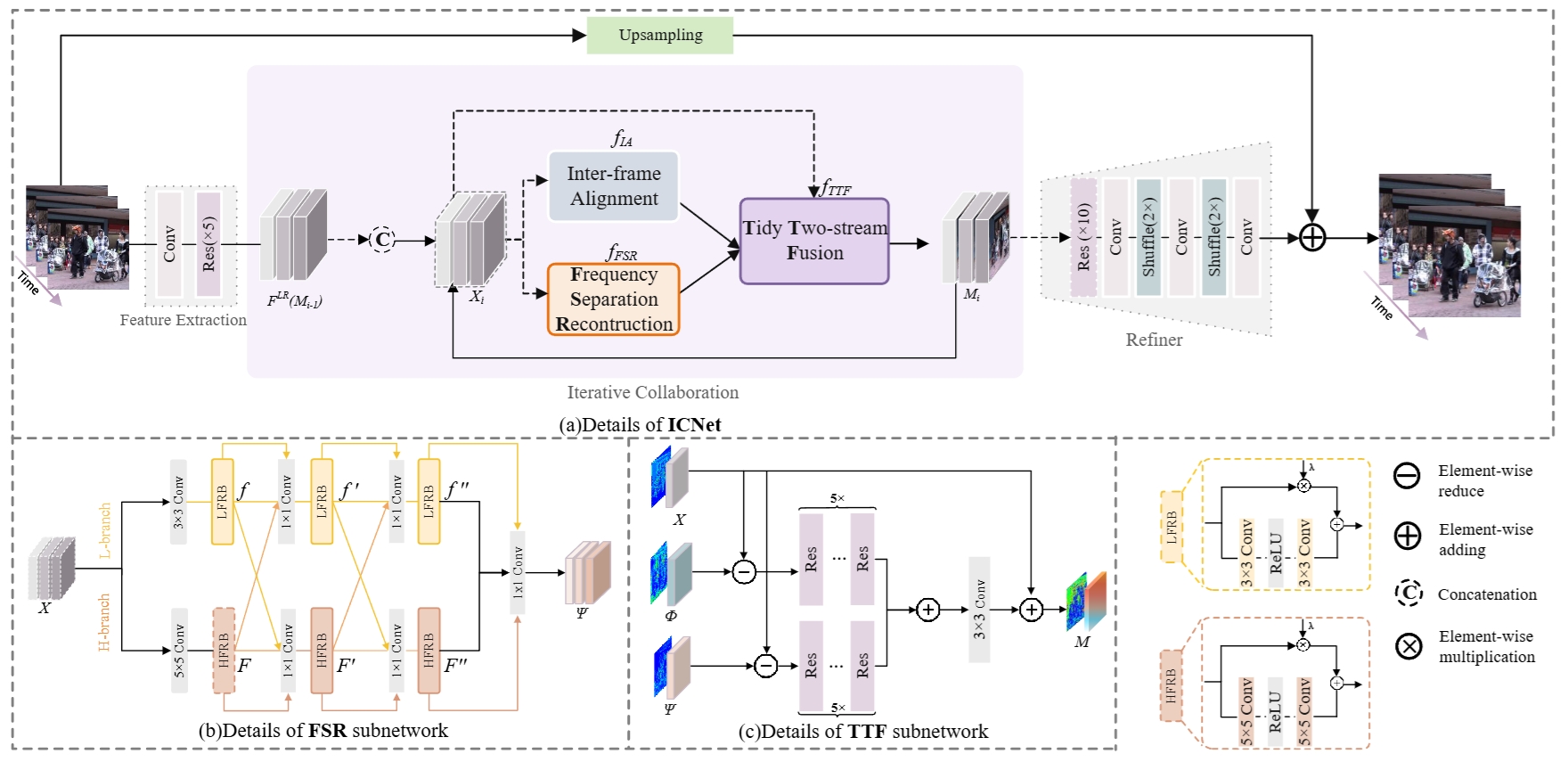
ICNet: Joint Alignment and Reconstruction via Iterative
Collaboration for Video Super-Resolution

Jiaxu Leng, Jia Wang, Xinbo Gao*, Bo Hu, Chengqiang Gao
Most previous frameworks either cost too much time or adopt some fixed modules resulting in alignment error in video super-resolution (VSR). In this paper, we propose a novel many-to-many VSR framework with Iterative Collaboration (ICNet), which employs the concurrent operation by iterative collaboration between alignment and reconstruction proving to be more efficient and effective than existing recurrent and sliding-window frameworks. With the proposed iterative collaboration, alignment can be conducted on super-resolved features from reconstruction while accurate alignment boosts reconstruction in return. In each iteration, the features of low-resolution video frames are first fed into the alignment and reconstruction subnetworks, which can generate temporal aligned features and spatial super-resolved features. Then, both outputs are fed into the proposed Tidy Two-stream Fusion (TTF) subnetwork that shares inter-frame temporal information and intra-frame spatial information without redundancy. Moreover, we design the Frequency Separation Reconstruction (FSR) subnetwork to not only model high-frequency and low-frequency information separately but also take benefit of each other for better reconstruction.
ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), 2022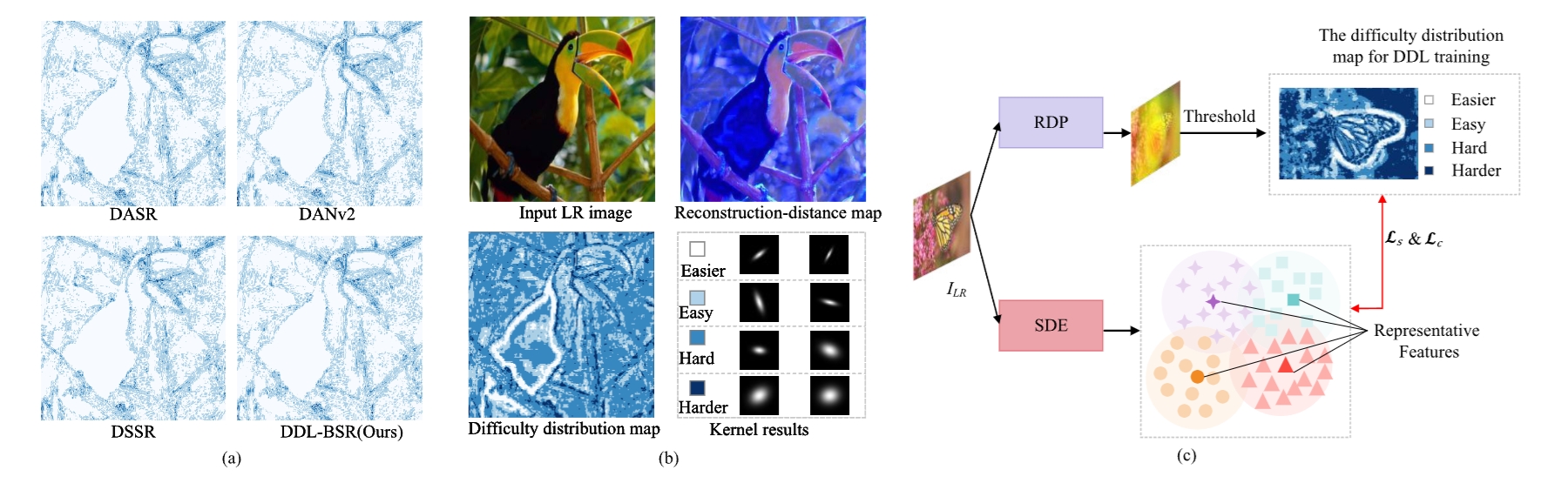
Difficulty-Guided Variant Degradation Learning for Blind Image
Super-Resolution

Jiaxu Leng, Jia Wang, Mengjingcheng Mo,Ji Gan, Wen Lu and Xinbo Gao*
Recent blind super-resolution (BSR) methods are explored to handle unknown degradations and achieve impressive performance. However, the prevailing assumption in most BSR methods is the spatial invariance of degradation kernels across the entire image, which leads to significant performance declines when faced with spatially variant degradations caused by object motion or defocusing. Additionally, these methods do not account for the human visual system’s tendency to focus differently on areas of varying perceptual difficulty, as they uniformly process each pixel during reconstruction. To cope with these issues, we propose a difficulty-guided variant degradation learning network for BSR, named difficulty-guided degradation learning (DDL)-BSR, which explores the relationship between reconstruction difficulty and degradation estimation. Accordingly, the proposed DDL-BSR consists of three customized networks: reconstruction difficulty prediction (RDP), space-variant degradation estimation (SDE), and degradation and difficulty-informed reconstruction (DDR). Specifically, RDP learns the reconstruction difficulty with the proposed reconstruction-distance supervision. Then, SDE is designed to estimate space-variant degradation kernels according to the difficulty map. Finally, both degradation kernels and reconstruction difficulty are fed into DDR, which takes into account such two prior knowledge information to guide super-resolution (SR).
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024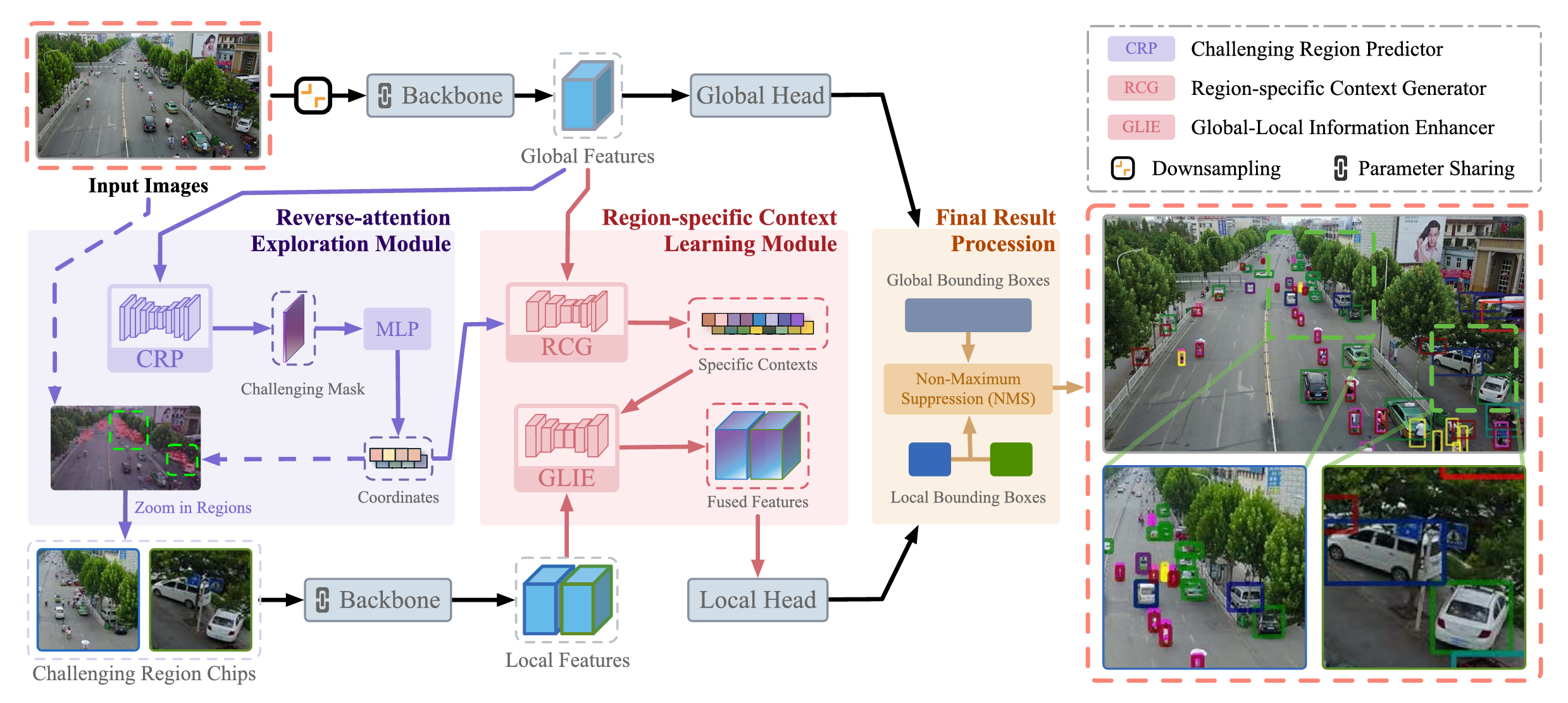
Pareto Refocusing for Drone-View Object Detection

Jiaxu Leng; Mengjingcheng Mo; Yinghua Zhou; Chenqiang Gao; Weisheng Li;
Xinbo Gao*
Drone-view Object Detection (DOD) is a meaningful but challenging task. It hits a bottleneck due to two main reasons: (1) The high proportion of difficult objects (e.g., small objects, occluded objects, etc.) makes the detection performance unsatisfactory. (2) The unevenly distributed objects make detection inefficient. These two factors also lead to a phenomenon, obeying the Pareto principle, that some challenging regions occupying a low area proportion of the image have a significant impact on the final detection while the vanilla regions occupying the major area have a negligible impact due to the limited room for performance improvement. Motivated by the human visual system that naturally attempts to invest unequal energies in things of hierarchical difficulty for recognizing objects effectively, this paper presents a novel Pareto Refocusing Detection (PRDet) network that distinguishes the challenging regions from the vanilla regions under reverse-attention guidance and refocuses the challenging regions with the assistance of the region-specific context. Specifically, we first propose a Reverse-attention Exploration Module (REM) that excavates the potential position of difficult objects by suppressing the features which are salient to the commonly used detector. Then, we propose a Region-specific Context Learning Module (RCLM) that learns to generate specific contexts for strengthening the understanding of challenging regions. It is noteworthy that the specific context is not shared globally but unique for each challenging region with the exploration of spatial and appearance cues.
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (IEEE TCSVT), 2022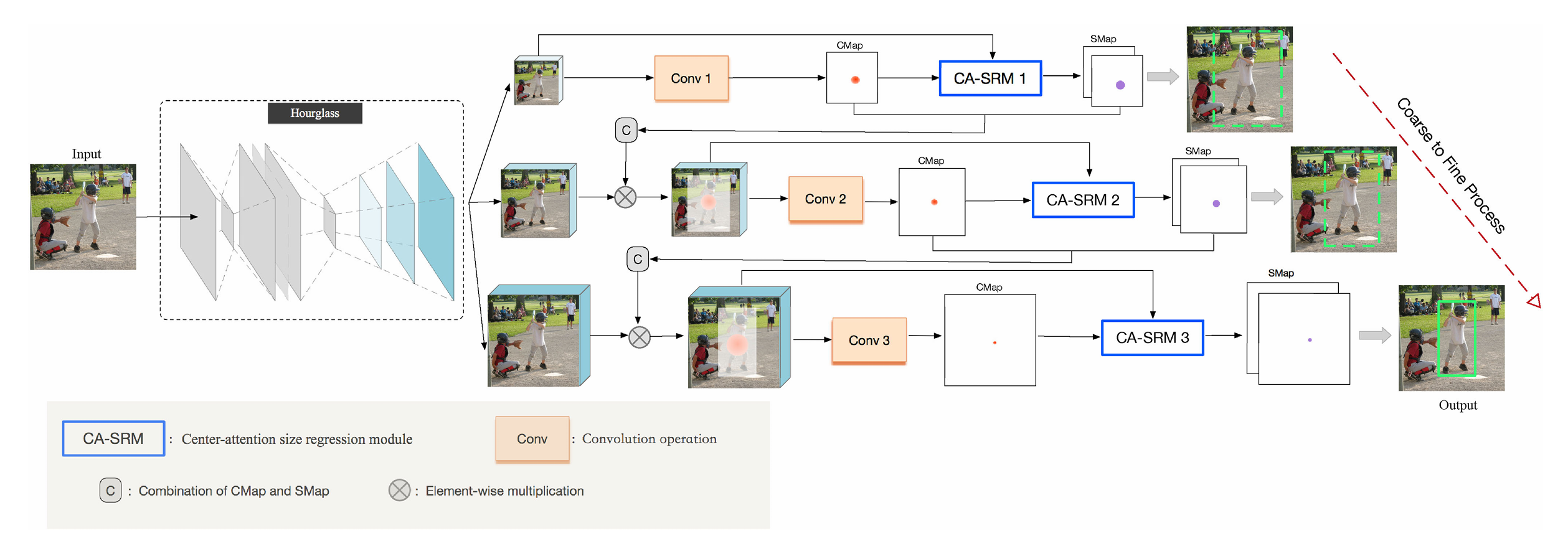
CrossNet: Detecting Objects as Crosses

Jiaxu Leng*; Ying Liu; Zhihui Wang; Haibo Hu; Xinbo Gao
With the use of deep learning, object detection has achieved great breakthroughs. However, existing object detection methods still can not cope with challenging environments, such as dense objects, small objects, and object scale variations. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel keypoint-based detection framework, called CrossNet, which significantly improves detection performance with minimal costs. In our approach, an object is modeled as a cross that consists of a center keypoint and a specific size, which eliminates the need of hand-craft anchor design. The proposed CrossNet outputs three types of maps: the center map, size map, and offset map, where both center map and offset map are to predict the center keypoints of objects and the size map is to estimate the sizes (width and height) of objects. Specifically, we first design a cascaded center prediction method that introduces a coarse-to-fine idea to improve center prediction. Furthermore, since center prediction considered as a classification task is easier than size regression relatively, we design a center-attention size regression module that uses the detection results of centers to assist the size prediction. In addition, a slightly modified hourglass network is designed to enhance the quality of feature maps for center and size prediction.
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (IEEE TMM), 2021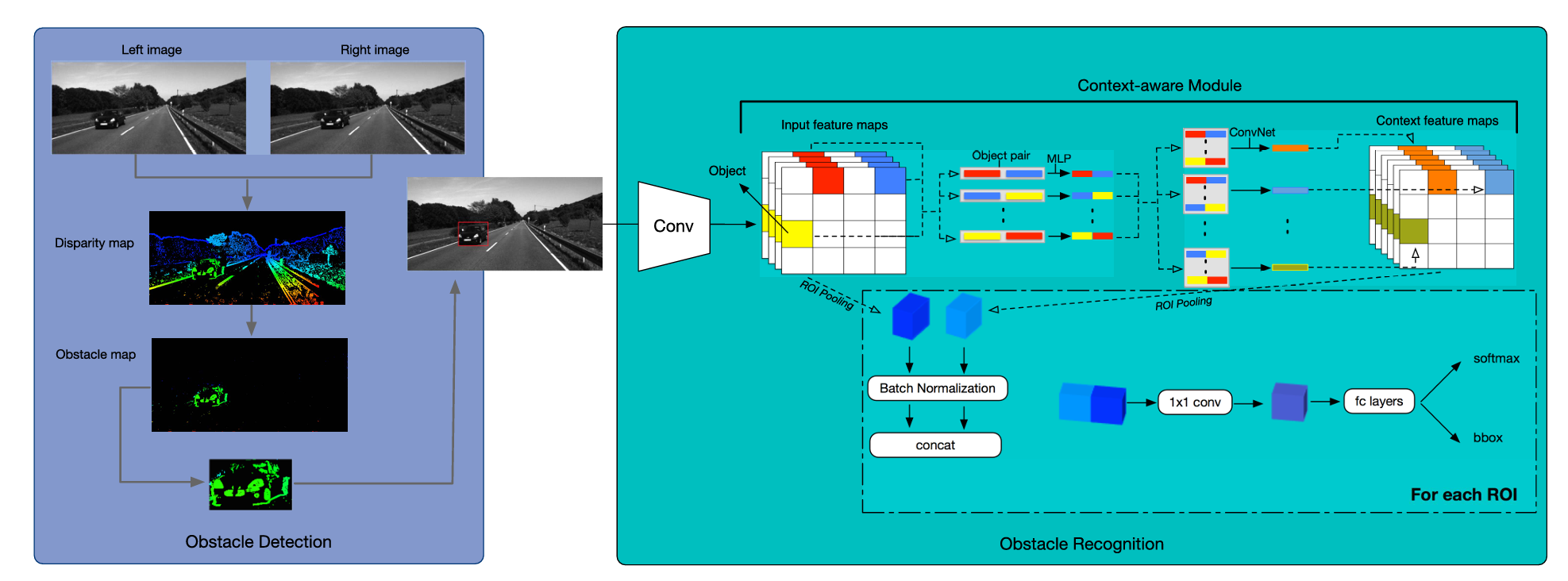
Robust Obstacle Detection and Recognition for Driver Assistance
Systems

Jiaxu Leng; Ying Liu*; Dawei Du; Tianlin Zhang; Pei Quan
This paper proposes a robust obstacle detection and recognition method for driver assistance systems. Unlike existing methods, our method aims to detect and recognize obstacles on the road rather than all the obstacles in the view. The proposed method involves two stages aiming at an increased quality of the results. The first stage is to locate the positions of obstacles on the road. In order to accurately locate the on-road obstacles, we propose an obstacle detection method based on the U-V disparity map generated from a stereo vision system. The proposed U-V disparity algorithm makes use of the V-disparity map that provides a good representation of the geometric content of the road region to extract the road features, and then detects the on-road obstacles using our proposed realistic U-disparity map that eliminates the foreshortening effects caused by the perspective projection of pinhole imaging. The proposed realistic U-disparity map greatly improves the detection accuracy of the distant obstacles compared with the conventional U-disparity map. Second, the detection results of our proposed U-V disparity algorithm are put into a context-aware Faster-RCNN that combines the interior and contextual features to improve the recognition accuracy of small and occluded obstacles. Specifically, we propose a context-aware module and apply it into the architecture of Faster-RCNN.
IEEE Transactions on Intellig Transportation Systems(IEEE TITS), 2020
Weixin Applet
Ipsum ipsum clita erat amet dolor justo diam
Chicken Burger $115
Ipsum ipsum clita erat amet dolor justo diam